《1 Introduction》
1 Introduction
Disruptive technology innovation plays an important role in the incubation, occurrence, and development of each technological and industrial revolution, and has a profound influence on social development and people’s lives [1]. At present, the world is on the verge of a new round of revolution in science and technology, and the disruptive technologies can develop quickly. The information, energy, and life science technologies intercross, integrate, permeate one another, and rise collectively. Disruptive technologies, such as additive manufacturing technology, IoT, mobile Internet, cloud computing, big data, and graphene are key to industrial breakthroughs [2,3]. All countries in the world aim to capitalize on the opportunities presented by this era, and have released strategic plans and policy measures that promote technological innovation and industry development. They also seek to seize the commanding heights in science and technology and the market opportunities available.
When a new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation occurs, China responds by accelerating the transformation of its economic development modes. The division of labor in the international industry is being reshaped. There is no significant improvement in the pace of industrial transformation in our country. Therefore, it should seize the major historical opportunities currently available to occupy the strategic high ground in the new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation.
Given this background, accurately forecasting the development trend of the disruptive technology that triggers industrial transformation provides support for the decision making required to frame major technology development plans and policies in our country and provides a point of reference for determining the priorities and fields of industrial transformation. To forecast the disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation, we can adopt the following approach. Study the connotation of the technology; use scientific and accurate methods to select disruptive technologies qualitatively and quantitatively; and summarize the characteristics and development patterns of the disruptive technology to explore technology forecasting.
The research on the connotation and qualitative and quantitative selection of disruptive technologies that lead to industrial transformation is a part of the “Research on and Forecasting of Major Disruptive Technologies That Trigger Industrial transformation” project. This is a major consulting project that was initiated by the Chinese Academy of Engineering in 2016. The project sticks to the innovative development concept and fulfills the guidelines for attaching importance to disruptive technology innovation put forward in the Fifth Plenary Session of the 18th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China. The guidelines are as follows: gather expert groups’ wisdom; absorb the latest research achievements in various fields at home and abroad; and select, put forward, and study disruptive technologies that are going to cause industrial transformation in the next 10 years, as well as disruptive technologies that will or may lead to industrial transformation in the next 20 years. In terms of the integration of industry and technology, the project describes the connotation of the disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation and establishes the index appraisal system for the disruptive technologies. More than 160 technologies are selected qualitatively in the first round of the questionnaire survey, and 26 technologies are selected quantitatively by using the index appraisal system in the second round of the questionnaire survey. This lays the foundation for studying further the relationship of disruptive technology and industrial transformation and carrying out technology forecasting.
《2 Connotation of disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation and index appraisal system》
2 Connotation of disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation and index appraisal system
《2.1 Connotation of disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation》
2.1 Connotation of disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation
The disruptive technology can be an original innovation based on new principle, an integrated innovation based on existing technology, or the transfer and innovative application of a mature technology. By achieving significant breakthroughs, disruptive technologies can replace existing technologies, have great application value, and are expected to have a far-reaching influence on developments in related fields. Based on technological innovation, industrial transformation gradually spreads to daily production and life [4] and further promotes the transformation of the industrial organization’s management, product manufacturing, and business operation mode. It even drives the emergence of new industries.
A disruptive technology causes industrial transformation that is based on the major breakthroughs of the technology. The product based on the technology with the disruptive innovation capability appeals to huge potential markets, and leads to transformations in the industry organization management, product manufacturing, and business operation mode.
Disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation have the following characteristics:
(1) Technological breakthroughs: These technologies lead to great breakthroughs in the innovative applications of scientific principles, integration and innovation of cross-disciplinary and cross-field technologies, or process engineering; these have significant impacts on the product performance or product models.
(2) Product substitution: After a technology makes an important breakthrough, the product with the technology that has the disruptive innovation capability is expected to trigger the upgrade of products and services (including the process equipment and design modes). In addition, a new product model may be developed.
(3) Market universality: The products or services with the disruptive technology gain market share from the existing products. Disruptive technologies drive the emergence of new markets and nurture them.
(4) Industrial transformation: There is an urgent need for products with disruptive technologies or new product models. The industry organization management, product manufacturing, and business operation mode related to the products must be adjusted or innovatively transformed.
《2.2 Index appraisal system for disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation》
2.2 Index appraisal system for disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation
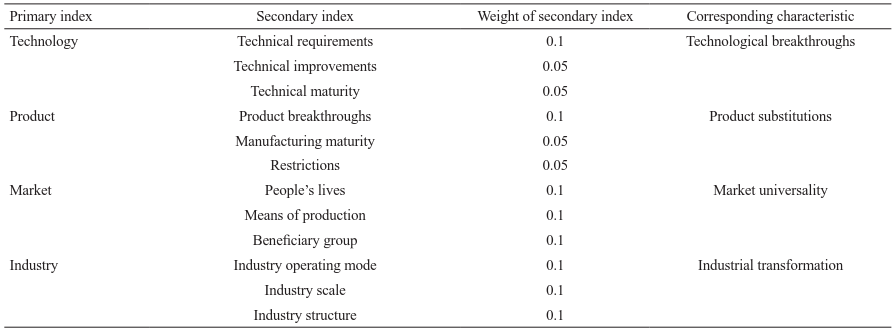
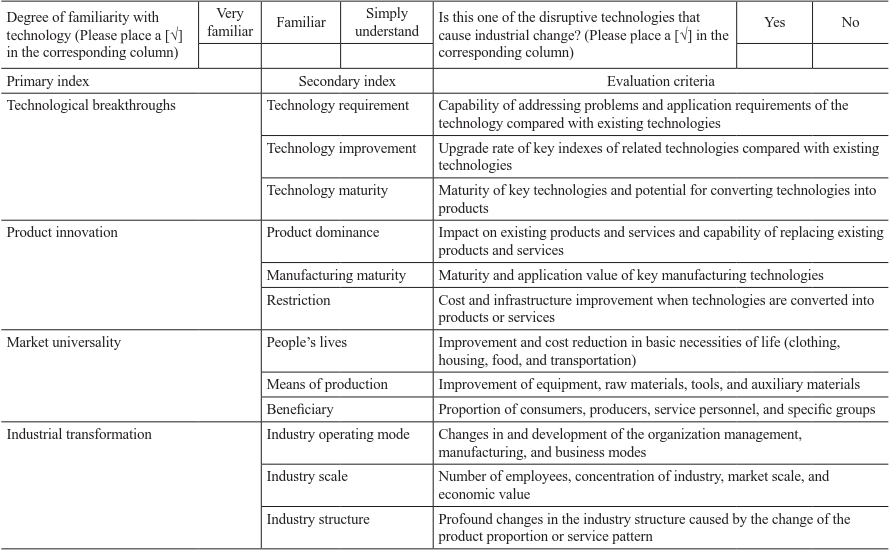
The index appraisal system is closely related to the connotation and characteristics of disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation. Four primary indexes and 12 secondary indexes are set. The four primary indexes correspond to the four characteristics of the disruptive technology that trigger industrial transformation—technology breakthrough, product substitution, market universality, and industrial transformation. In addition, an initial weight is assigned to each secondary index (Table 1) to provide a suitable method for the quantitative selection of disruptive technologies.
《Table 1》
Table 1. Disruptive technology index appraisal system.
The quantitative criteria can be set for each secondary index, and a score ranging from 0 to 10 points is assigned, based on the evaluation criteria.
2.2.1 Technical requirements
“Requirements” reflect the fact that technologies can solve critical problems. This index can be used to determine whether there is a strong demand for applying and promoting a technology (Table 2).
《Table 2》
Table 2. Evaluation criteria of the technical requirement index.

2.2.2 Technical improvement index
This index indicates the improvement of core indexes of the key technologies. The higher the upgrade rate of the index, compared with that of existing technologies, the more obvious the disruptive impact (Table 3).
《Table 3》
Table 3. Evaluation criteria of the technical improvement index.

2.2.3 Technical maturity index
The index indicates the maturity of key technologies. The greater the maturity of a technology, the greater the potential of it being converted into products. The study focuses on disruptive technologies that lead to industrial transformation within 10 years. It takes a certain period of time to cultivate technologies,convert technologies into products, and launch products in the market. Therefore, only those technologies with a maturity (TRL) score equal to, or greater than, 4 are considered (Table 4).
《Table 4》
Table 4. Evaluation criteria of the technical maturity index.

2.2.4 Product prominence index
This index indicates the substitution effect and impact on old products or services of the products or services associated with disruptive technologies. The higher the score of the index, the higher the probability of product substitution (Table 5).
《Table 5》
Table 5. Evaluation criteria of the product prominence index.

2.2.5 Manufacturing maturity index
This index indicates the maturity of key manufacturing technologies during the product manufacturing and the manufacturing risks during the conversion from technologies into products. The higher the manufacturing maturity, the greater the application value (Table 6).
《Table 6》
Table 6. Evaluation criteria of the manufacturing maturity index.

2.2.6 Restriction index
This index indicates the efforts required to convert technologies into products or services. This index is the only negative index, and covers the cost, infrastructure, and policies involved. The higher the score of the index, the greater the potential for converting technologies into products or services (Table 7).
《Table 7》
Table 7. Evaluation criteria of the restriction index.
2.2.7 People’s lives index
The index indicates the impact of disruptive technologies on the means of livelihood (consumer) market. It reflects changes and improvements in the basic necessities of life (clothing, housing, food, and transportation) and even spiritual activities, such as social entertainment; it also includes the reduction in cost of the basic necessities of life and the spiritual level (Table 8).
《Table 8》
Table 8. Evaluation criteria of the people’s lives index.

2.2.8 Means of production index
This index indicates the impact of disruptive technologies on the “means of production” markets. It reflects the changes in means of production, such as equipment, raw materials, tools, and auxiliary materials; the various markets covered are commodity manufacturing, industrial production, farming, and weapon and equipment development (Table 9).
《Table 9》
Table 9. Evaluation criteria of the means of production index.
2.2.9 Beneficiary index
This index indicates the impact of disruptive technologies on consumers, including common consumers (ordinary people), producers, service personnel (production and manufacturing, agriculture, and services) and specific groups (military personnel and others). The higher the index score, the greater the impact of disruptive technologies on consumers (Table 10).
《Table 10》
Table 10. Evaluation criteria of the beneficiary index.

2.2.10 Industry operating mode index
This index reflects the development and changes of industry operating modes, including the organization management mode, manufacturing mode, and business mode (Table 11).
《Table 11》
Table 11. Evaluation criteria of the industry operating mode index.

2.2.11 Industry scale index
This index reflects the enlargement and changes of the industry scale in terms of the number of employees, concentration of industry, market scale, and economic value (Table 12).
《Table 12》
Table 12. Evaluation criteria of the industry scale index.
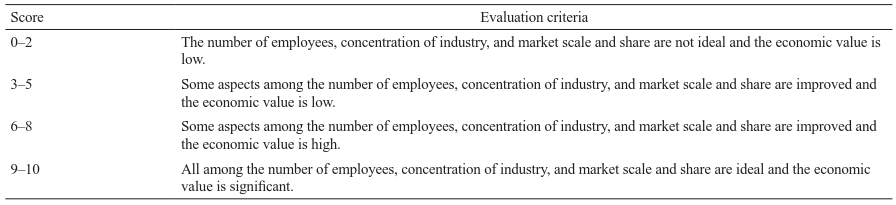
2.2.12 Industry structure index
This index reflects the profound changes in the industry structure caused by the change in the product market share or service pattern. New industries will emerge, existing industries will be reformed, and sunset industries will be eliminated (Table 13).
《Table 13》
Table 13. Evaluation criteria of the industry structure index.

《3 Qualitative selection of disruptive technologies》
3 Qualitative selection of disruptive technologies
The qualitative selection of disruptive technologies is completed through the following steps: (1) create a technology list based on various disruptive technology research reports and hotspot technologies at home and abroad; (2) conduct a questionnaire survey intended for academicians and experts; and (3) develop a list of technologies (165 technologies) to be studied according to the result of the questionnaire survey (Fig. 1).
《Fig. 1》

Fig. 1. Flow for qualitatively selecting disruptive technologies.
《3.1 Technology list》
3.1 Technology list
Continuously track the disruptive technology research and forecasting reports of major countries and institutions and sort out industry-related disruptive technologies. Sort the domestic disruptive technology-related policies and hotspot technologies,and filter and classify the disruptive technologies involved. Finally, create the technology list based on the 313 technologies that constitute the research on China’s engineering science and technology 2035 development strategy and some achievements released in the technical forecast for the 13th Five-Year Plan released by the Ministry of Science and Technology.
《3.2 First round of questionnaire survey》
3.2 First round of questionnaire survey
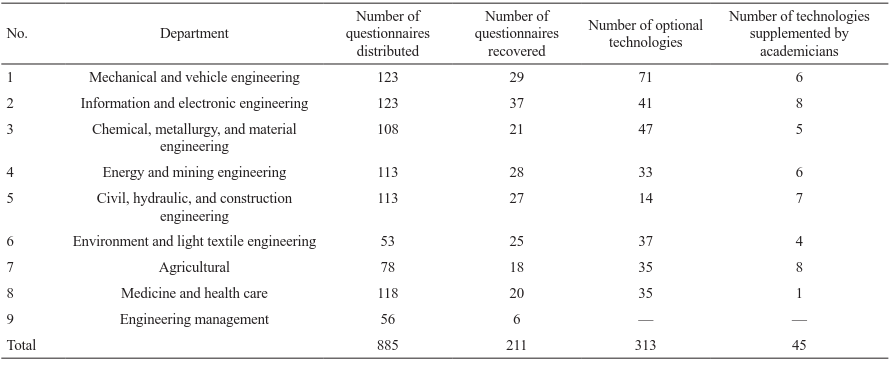
The questionnaire survey seeks to collect the opinions of academicians in different departments. Eight different technology lists are distributed. From each list, the academicians select no more than 20 disruptive technologies that can lead to industrial transformation. In addition, they can also supplement disruptive technologies. On the basis of responses in the collected questionnaires, technologies are ranked according to the number of times they are selected; the number of technologies selected by academicians and experts from different departments are listed in Table 14.
《Table 14》
Table 14. Statistics on questionnaires in the first round of survey.
《3.3 List of technologies to be studied further》
3.3 List of technologies to be studied further
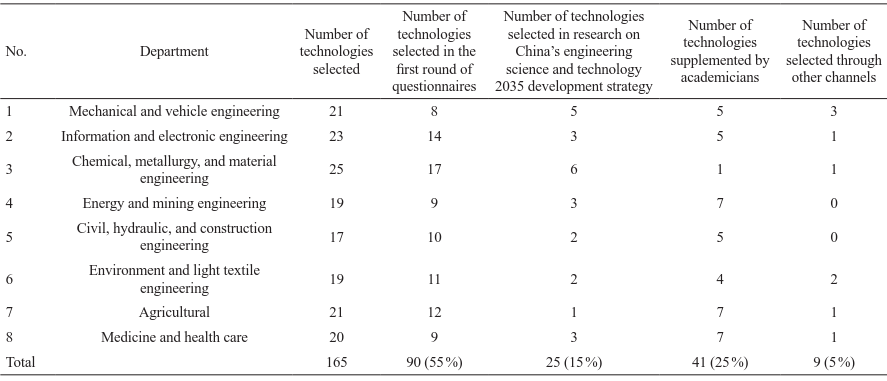
Based on the technologies selected in the first round of questionnaire survey, technologies selected during research on China’s engineering science and technology 2035 development strategy, latest hotspot technologies at home and abroad, and the technologies supplemented by academicians, we create a list of technologies to be studied (165 technologies) in greater detail (Table 15). In addition, the statistics are collected on the years in which the technologies are expected to be implemented (Table 16).
《Table 15》
Table 15. Origin of the listed technologies.
《Table 16》
Table 16. Time frame during which technologies are expected to be implemented.

《4 Quantitative selection of disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation》
4 Quantitative selection of disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation
On the basis of the list of technologies to be studied further (165 technologies), the second round of questionnaire survey is designed by using the index appraisal system. The survey is intended for academicians of different departments. Based on the survey results and the technologies supplemented by the academicians, a list of about 20 major disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation is created (Fig. 2).
《Fig. 2》
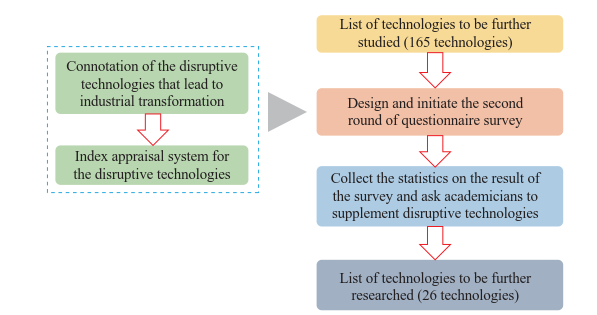
Fig. 2. Flowchart for quantitatively selecting disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation.
Table 17 shows the flow for quantitatively selecting disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation. The following solution is provided for collecting statistics from the questionnaire survey:
(1) For technologies that the academicians are very familiar with, familiar with, and simply understand, the scores assigned are in the proportion 3:2:1, respectively.
(2) The technologies not identified as disruptive technologies are excluded from the survey result statistics.
(3) If an academician only fills in “familiarity” for a technology but does not evaluate the technology, the technology is considered when counting the number of selected technologies but not when its score is being counted.
(4) If an academician does not fill in “familiarity” with a technology, the technology is considered as one that the academician just understands.
《Table 17》
Table 17. Settings for selecting single technologies in the second round of the questionnaire survey.
Technology 1: a particular technology
In the second round of the questionnaire survey, there were 178 valid responses, giving a recovery rate close to 20 %. The technologies are ranked by their scores and selection count, and 29 technologies are supplemented by academicians. Finally, a preliminary list of disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation is created (currently, there are 26 disruptive technologies). The final list of technologies to be studied further is developed based on the results of various workshops.
The 26 disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation are: autonomous and unmanned technology; new energy automobile technology; block-chain/digital currency technology; intelligent computing and intelligent software; development and utilization of big data; artificial intelligence and brain-related technology; 3D printing; superconducting technology; nanotechnology oriented to super-high energetic conversion and storage;carbon-based material manufacturing, such as carbon nanotubes and graphene; new-generation nuclear reactor technology; Internet of energy; large-scale, safe, and economic exploitation of natural gas hydrate; new electronic storage; downhole oil-water separation with well injection-production; numerical weather prediction; 3D printing for construction engineering; modern and efficient water-saving irrigation; super high-speed rail; intelligent manufacturing of textiles; new pesticides; crop breeding; gene editing; health medicine; biological medicine; and chronic disease prevention & control engineering and treatment.
《5 Conclusions》
5 Conclusions
In this project, the connotation of disruptive technologies that trigger industrial transformation is studied; an index appraisal system is established for these technologies; and two rounds of questionnaire surveys are administered to academicians. A list of 165 technologies is selected qualitatively from 313 technologies, and 26 technologies that will be studied further are selected quantitatively. Based on the research on the connotation and selection of the disruptive technologies that lead to industrial transformation, we make a preliminary exploration of the relations between disruptive technologies and industrial transformation; this lays the foundation for technology forecasting in the later stage of the project.
During the research on the connotation and selection of the disruptive technologies that lead to industrial transformation, the project also focuses on the accumulation of stage-wise achievements and the innovation of research methods. For example, in this project, three typical cases of disruptive technologies are selected. The methods for identifying disruptive technologies outside China are selected and compared; in addition, we have conducted symposiums with well-known enterprises in various fields. We have also communicated with government agencies and military experts on the development trend of disruptive technologies, measures taken by the government to support disruptive technologies, and the dual use of the technologies.
In further research on the connotation and selection of the disruptive technologies that lead to industrial transformation, we need to: identify the granularity of each technology included in the various lists; better identify the potential of disruptive technologies in the incubation stage; and ensure that questionnaires are distributed to a larger number of experts across industries. Therefore, we need to draw on our experience in conducting research on the connotation and selection of the disruptive technologies that lead to industrial transformation, develop reasonable, scientific, and innovative technology selection mechanisms, and establish technology databases to better forecast and analyze disruptive technologies.














 京公网安备 11010502051620号
京公网安备 11010502051620号